44 coupon rate and yield to maturity
Difference Between Current Yield and Coupon Rate (With Table) The main difference between the current yield and coupon rate is that the current yield is just an expected return from a bond, and the coupon rate is the actual amount paid regularly for a bond till it gets mature. The Current Yield keeps changing as the market value of the bond changes, but the Coupon Rate of a particular bond remains the ... Bond Yield to Maturity (YTM) Calculator - DQYDJ This makes calculating the yield to maturity of a zero coupon bond straight-forward: Let's take the following bond as an example: Current Price: $600. Par Value: $1000. Years to Maturity: 3. Annual Coupon Rate: 0%. Coupon Frequency: 0x a Year. Price =. (Present Value / Face Value) ^ (1/n) - 1 =.
Bond's Price, Coupon Rate, Maturity | CFA Level 1 - AnalystPrep Relationships Among a Bond's Price, Coupon Rate, Maturity, and Market Discount Rate. 27 Sep 2019. Price versus Market Discount Rate (Yield-to-maturity) The price of a fixed-rate bond will fluctuate whenever the market discount rate changes. This relationship could be summarized as follows:
Coupon rate and yield to maturity
Concept 82: Relationships among a Bond's Price, Coupon Rate, Maturity ... Percentage price change is more when discount rate goes down than when it goes up by the same amount. Relationship with coupon rate. A bond is priced at a premium above par value when the coupon rate is greater than the market discount rate. A bond is priced at a discount below par value when the coupon rate is less than the market discount rate. Impact of the coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM) Describe the impact of the coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM) on bond par value and market value. If you were the CFO of a company and the Federal Reserve Bank decided to increase the interest rate by 1% beginning next quarter, what steps would you take to raise capital from the financial markets? Coupon Rate - Learn How Coupon Rate Affects Bond Pricing Coupon Rate vs. Yield-to-Maturity. The coupon rate represents the actual amount of interest earned by the bondholder annually, while the yield-to-maturity is the estimated total rate of return of a bond, assuming that it is held until maturity. Most investors consider the yield-to-maturity a more important figure than the coupon rate when ...
Coupon rate and yield to maturity. Bond's Maturity, Coupon, and Yield Level - AnalystPrep Longer maturity bond prices are more sensitive to changes in yields than shorter maturity bonds. As shown in the following graph, the price of the 30-year bond increases a lot more than that of the 1-year bond in response to a decrease in interest rates. Coupon Rate. Bonds with higher coupon rates are less sensitive to changes in interest rates. Coupon Rate - Meaning, Example, Types | Yield to Maturity Comparision Therefore, if the 5-Year Treasury Yield becomes 4%, still the coupon rate will remain 5%, and if the 5-Year Treasury Yield increases to 12% yet, the coupon rate will remain 10%. Coupon Rate Vs. Yield to Maturity. Many people get confused between coupon rate and yield to maturity. In reality, both are very different measures of returns. Yield to Maturity vs Coupon Rate: What's the Difference What Is the Coupon Rate? A bond's coupon rate is the fixed percentage of interest you will earn on an annual or semi-annual basis once you purchase it up until the maturity date (the date the bond issuer agrees to repay its investor by when it is purchased). For example, if you take out a $1,000 bond with a coupon rate of 4% and it has an ... Basics Of Bonds - Maturity, Coupons And Yield Current yield is the bond's coupon yield divided by its market price. To calculate the current yield for a bond with a coupon yield of 4.5 percent trading at 103 ($1,030), divide 4.5 by 103 and multiply the total by 100. You get a current yield of 4.37 percent. Say you check the bond's price later and it's trading at 101 ($1,010).
What Is a Coupon Rate? How To Calculate Them & What They're Used For Coupon rates can be determined by dividing the sum of the annual coupon payments by the actual bond's face value. However, this is not the same as the interest rate. For instance, a bond with a face value of $5,000 and a coupon of 10%, pays $500 every year. However, if you buy a bond above its face value, let's say at $7,000, you will get a ... Answered: A bond with a coupon rate of 10 percent… | bartleby Q: Consider BOND AAA Coupon rate: 9,4% per year Yield to maturity: 10,6% per year Settlement date: 16… A: Coupon rate 9.4% Settlement date is 16 july 2022 Maturity date is 9 october 2048 To Find: Accured… Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity (With Table) Coupon rate can be stated as the sum of money which a bond issuer has to pay relative to its bond value, while Yield to Maturity (YTM) can be defined as the total money which is to be accepted by an individual after the maturation. The coupon rate is also known as "Yield from the Bond.". This term is used to complicate things at some point ... Yield To Maturity - Bond Yield - recentlyheard.com The yield to maturity is the overall rate of return, over the life of the bond based on many of the factors above. A fixed income security is sold based on current interest rates vs. the interest rate on the bond. This difference is why bonds are sold at premiums (above par) and at a discount (below par). If a security has a nominal yield of 6% ...
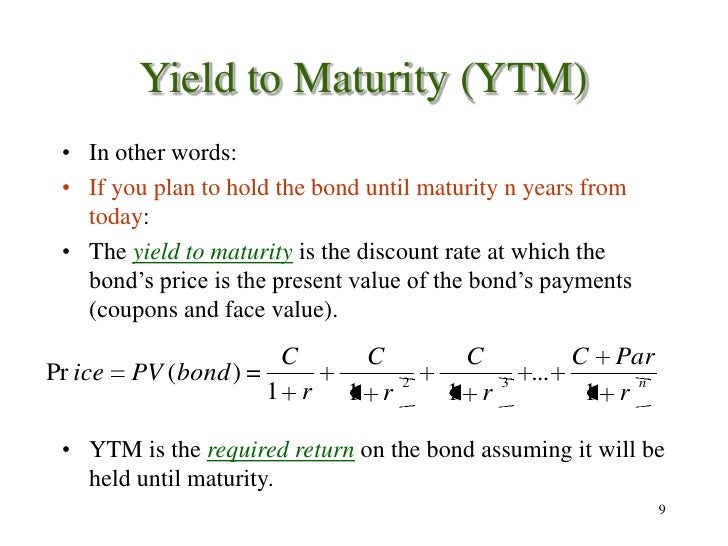
Coupon vs Yield | Top 8 Useful Differences (with Infographics) 3. Interest rates influence the coupon rates. The current yield compares the coupon rate to the market price of the bond. 4. The coupon amount remains the same until maturity. Market price keeps on fluctuating, better to buy a bond at a discount which represents a larger share of the purchase price. 5. Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Overview, Formula, and Importance The coupon rate Coupon Rate A coupon rate is the amount of annual interest income paid to a bondholder, based on the face value of the bond. for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years. The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below: The approximated YTM on the bond is 18.53%. Importance of Yield to Maturity Question 6 Required rate of return (market interest | Chegg.com Finance questions and answers. Question 6 Required rate of return (market interest rate or yield to maturity) >Coupon ra bond will be valued at a) Premium b) Par value c) Discount d) None of the above. Question 7 A bond is said to be issued at premium when UNR a) Coupon rate>Required returns b) Coupon rate=Required returns c) Coupon rate d ... Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield of Maturity Coupon Rate. Yield of Maturity. 1. The amount paid by the issuer to the bondholder until it's maturity is called coupon rate. The yield of maturity means the total return earned by the investor until it's maturity. 2. The rate of interest is paid annually at a coupon rate.
Yield to Maturity vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? The yield to maturity is the estimated annual rate of return for a bond assuming that the investor holds the asset until its maturity date and reinvests the payments at the same rate. The coupon ...
Coupon vs Yield | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) The yield of a bond changes with a change in the interest rate in the economy, but the coupon rate does not have the effect of the interest rate. Recommended Articles. This has been a guide to the Coupon vs. Yield. Here we discuss the top differences between coupon rate and yield to maturity along with infographics and a comparison table.
Difference Between Yield to Maturity and Coupon Rate The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest earned by the bondholder, which is expressed as a percentage of the nominal value of the bond. 1. Overview and Key Difference.
Describe the impact of the coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM) on ... Describe the impact of the coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM) on bond par value and market value. If you were the CFO of a company and the Federal Reserve Bank decided to increase the interest rate by 1% beginning next quarter, what steps would you take to raise capital from the financial markets?
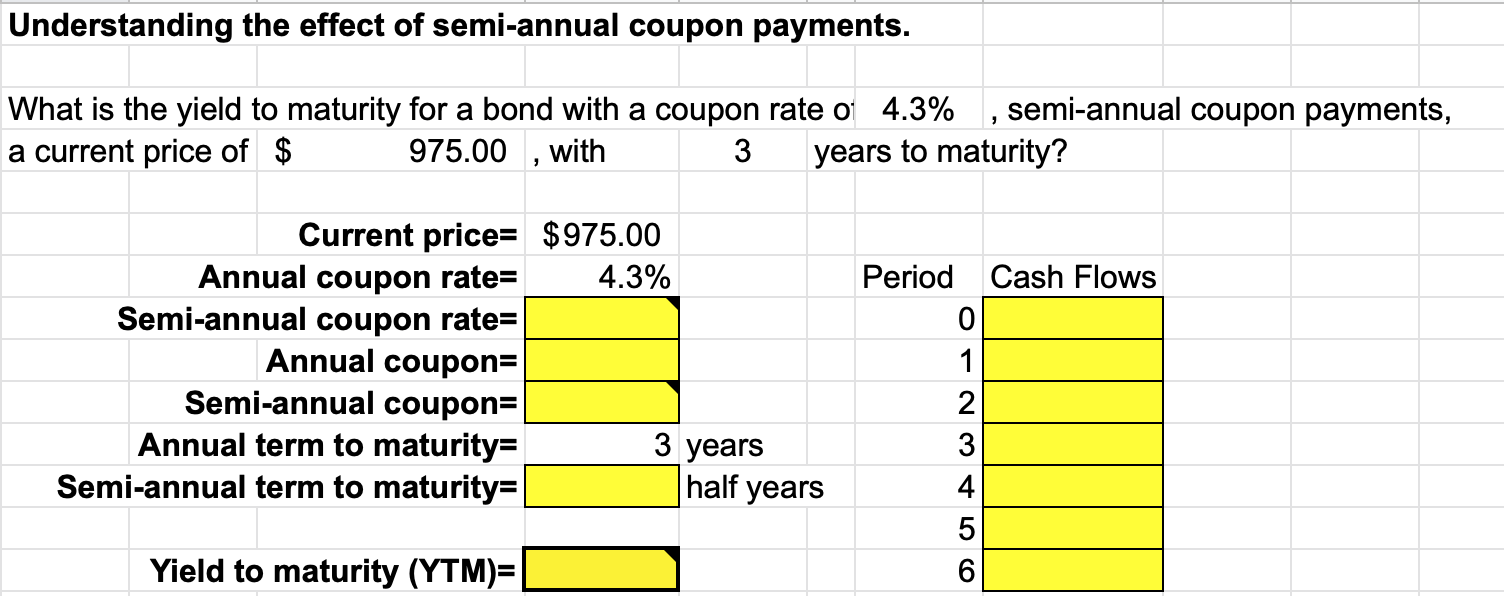
Yield to Maturity Calculator | Good Calculators C is the periodic coupon payment, r is the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond, B is the par value or face value of a bond, Y is the number of years to maturity. Example 2: Suppose a bond is selling for $980, and has an annual coupon rate of 6%. It matures in five years, and the face value is $1000. What is the Yield to Maturity?
Coupon Rate - Meaning, Calculation and Importance This article explains the coupon rate for bonds, its calculation, importance and difference between coupon rate and yield to maturity in detail. What is Coupon Rate in Bonds? The coupon rate for bonds is the interest bond issuer pays on the face value of the bond. In other words, it is the periodic interest that the issuer of the bond pays the ...
Coupon Rate Formula | Step by Step Calculation (with Examples) The yield to maturity (YTM) refers to the rate of interest used to discount future cash flows. read more will increase because an investor will be willing to purchase the bond at a higher value. A bond trades at par when the coupon rate is equal to the market interest rate. Recommended Articles. This has been a guide to what is Coupon Rate Formula.
Important Differences Between Coupon and Yield to Maturity Coupon vs. Yield to Maturity . A bond has a variety of features when it's first issued, including the size of the issue, the maturity date, and the initial coupon. For example, the U.S. Treasury might issue a 30-year bond in 2019 that's due in 2049 with a coupon of 2%. ... Yield to maturity will be equal to coupon rate if an investor purchases ...
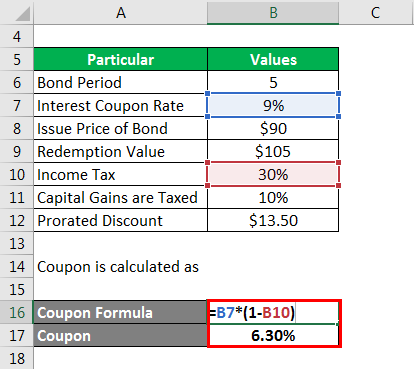
Coupon Rate: Formula and Bond Nominal Yield Calculator Coupon Rate = Annual Coupon / Par Value of Bond. For example, if the coupon rate on a bond is 6% on a $100k bond, the coupon payment comes out to $6k per year. Par Value = $100,000. Coupon Rate = 6%. Annual Coupon = $100,000 x 6% = $6,000. Since most bonds pay interest semi-annually, the bondholder receives two separate coupon payments of $3k ...
What Is the Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield-To-Maturity? Coupon rate is expressed as the percentage (per annum basis) of the face value of the bond. It is the amount that the bondholders will receive for holding the bond. Coupon payments are usually made semi-annually or quarterly. Yield-to-maturity (YTM), as the name states, is the rate of return that the investor/bondholder will receive, assuming ...
Understanding Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity of Bonds The Yield to Maturity is a rate of return that assumes that the buyer of the bond will hold the security until its maturity date and incorporates the rise or fall of market interest rates. This will be a bit technical. ... Coupon Rate: Maturity Date: Coupon Frequency: YTM: Face Value: Clean Price: Market Value: RTB 03-11: 2.375%: 3/9/2024: 4: 2 ...
Coupon Rate - Learn How Coupon Rate Affects Bond Pricing Coupon Rate vs. Yield-to-Maturity. The coupon rate represents the actual amount of interest earned by the bondholder annually, while the yield-to-maturity is the estimated total rate of return of a bond, assuming that it is held until maturity. Most investors consider the yield-to-maturity a more important figure than the coupon rate when ...
Impact of the coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM) Describe the impact of the coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM) on bond par value and market value. If you were the CFO of a company and the Federal Reserve Bank decided to increase the interest rate by 1% beginning next quarter, what steps would you take to raise capital from the financial markets?
Concept 82: Relationships among a Bond's Price, Coupon Rate, Maturity ... Percentage price change is more when discount rate goes down than when it goes up by the same amount. Relationship with coupon rate. A bond is priced at a premium above par value when the coupon rate is greater than the market discount rate. A bond is priced at a discount below par value when the coupon rate is less than the market discount rate.

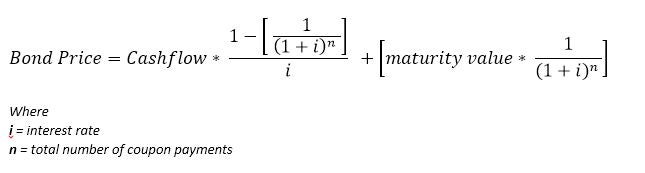







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)
Post a Comment for "44 coupon rate and yield to maturity"